Automate Spreadsheet Data Processing & Streamline Data Workflows
Automate spreadsheet data ingestion, transformation (like calculating age), and storage across multiple platforms, saving hours of manual data preparation each week.
Manually processing spreadsheet files across different sources and formats is tedious and error-prone, consuming valuable time. This n8n workflow automates the entire lifecycle of spreadsheet data, from loading and transforming to saving, ensuring accuracy and freeing up your team for critical tasks.
Documentation
Efficient Spreadsheet Data Management with n8n
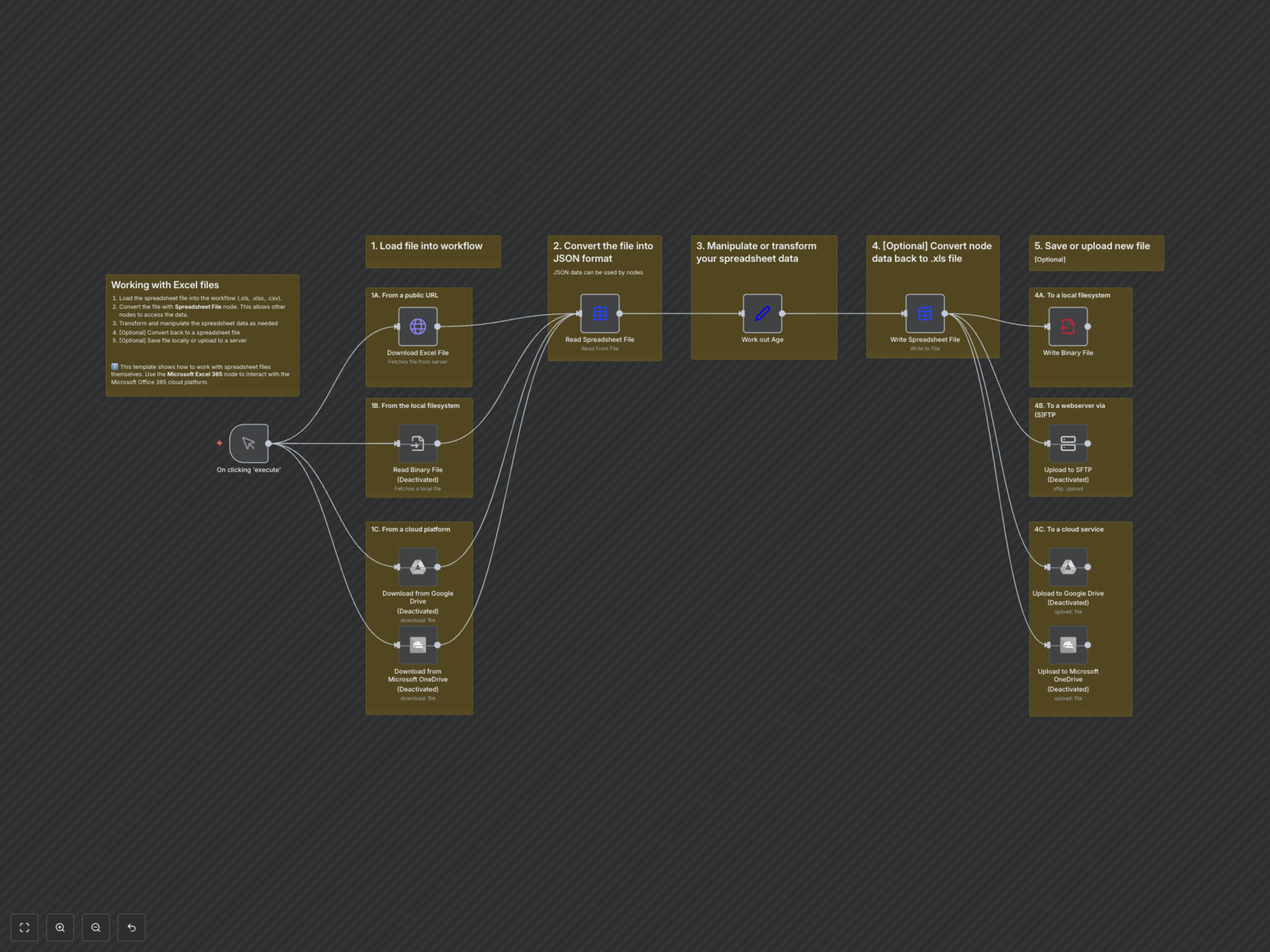
This workflow provides a comprehensive framework for handling spreadsheet files, including Excel (.xlsx, .xls) and CSV formats, within n8n. It demonstrates how to load files from diverse sources, convert them for easy manipulation, perform data transformations (such as calculating age from dates), and save the processed data to various destinations, both locally and in the cloud.
Key Features
- Flexible file loading from public URLs, local storage, Google Drive, and OneDrive.
- Seamless conversion of spreadsheet files into accessible JSON format for powerful data manipulation.
- Automated data transformation, including calculated fields like age from existing date data.
- Effortless conversion back to spreadsheet format (.xlsx) and saving to local filesystems, SFTP servers, Google Drive, or OneDrive.
How It Works
The workflow begins with a manual trigger, allowing you to choose your input method: download a file from a public URL, read from a local path, or fetch from cloud storage like Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive. Once loaded, the Spreadsheet File node converts the binary file into structured JSON data. This JSON data is then passed to a Set node where you can perform transformations, such as calculating an 'age' field based on a 'created' date. Finally, the processed data is converted back into a new spreadsheet file (e.g., .xlsx) and can be written to your local filesystem or uploaded to various cloud services or an SFTP server.