Accelerate LLM Workflows: Master Chaining for Web Insights
Implement diverse LLM chaining patterns to reduce web content analysis time by up to 70% with parallel processing, delivering faster and richer insights.
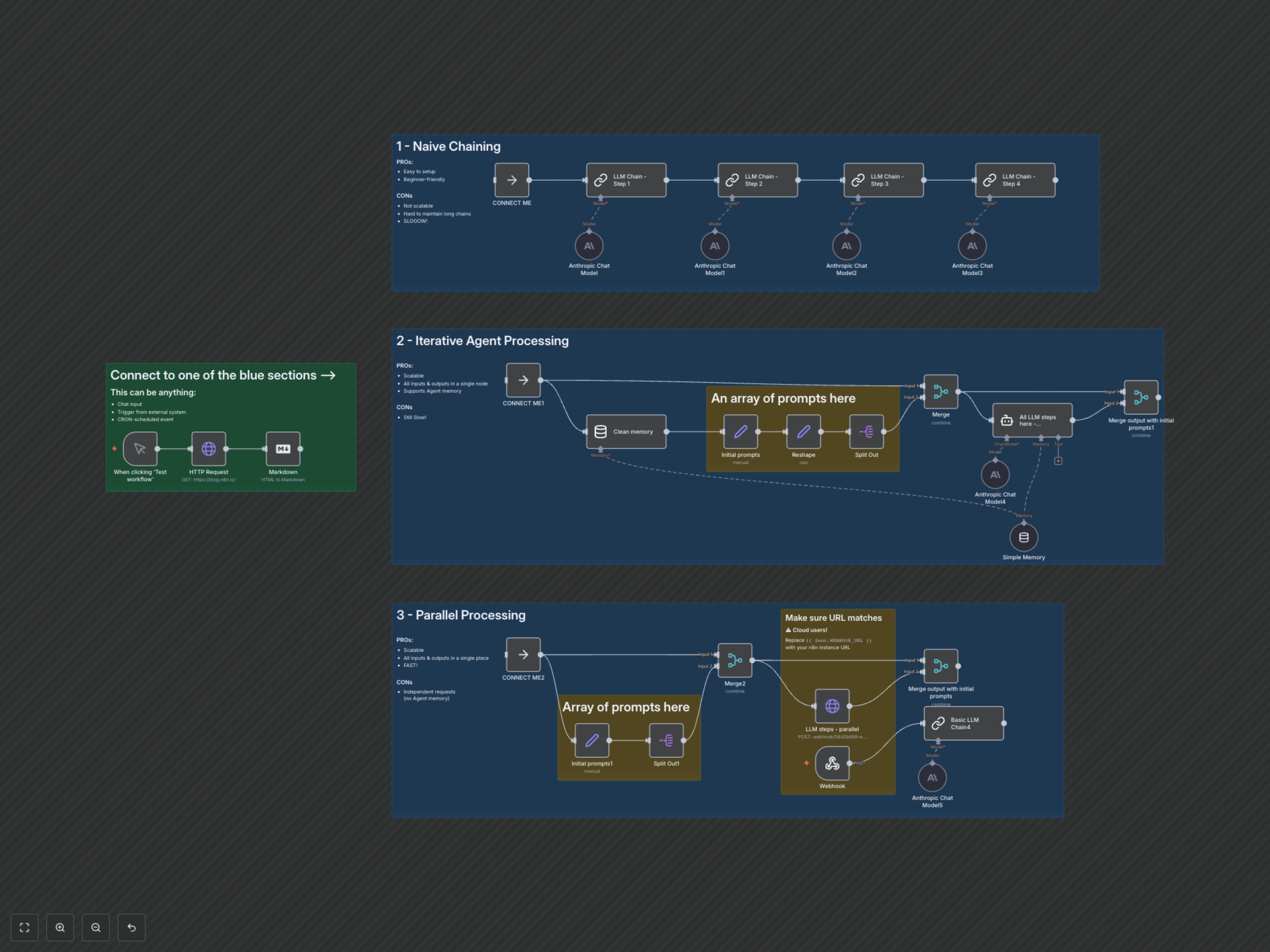
Manual content analysis and sequential AI processing on web pages are time-consuming and lack scalability. This n8n workflow demonstrates three powerful LLM chaining strategies—naive, iterative agent, and parallel—to efficiently extract insights, summarize, and generate creative content from any URL.
Documentation
Master LLM Chaining for Web Content Analysis
Efficiently extract, summarize, and transform information from any web page using advanced Large Language Model chaining techniques. This workflow provides practical examples for implementing naive, iterative agent, and high-speed parallel LLM processing within n8n.
Key Features
- Seamlessly fetch and convert web page content to markdown for LLM processing.
- Explore and compare three distinct LLM chaining strategies: Naive Sequential, Iterative Agent with Memory, and High-Performance Parallel processing.
- Extract specific data points like authors and posts, summarize content, or generate creative responses (e.g., jokes) from web pages.
- Leverage Anthropic's Claude models (via LangChain) for intelligent content understanding and generation.
- Gain insights into designing scalable and efficient AI workflows using n8n's visual builder.
How It Works
This workflow begins by fetching HTML content from a specified URL and converting it to Markdown. It then branches into three distinct sections, each showcasing a different LLM chaining strategy:
- 1. Naive Chaining: Processes multiple prompts sequentially, passing the full web content to each LLM call. This method is straightforward but can be slow and resource-intensive for longer chains.
- 2. Iterative Agent Processing: Utilizes an n8n Agent node with a LangChain memory buffer to process a series of prompts iteratively, maintaining conversational context. This approach is more scalable and maintains memory but still processes steps sequentially.
- 3. Parallel Processing: Divides multiple prompts into independent tasks and sends them to the LLM concurrently via a webhook, drastically accelerating execution. This method offers the fastest results but does not maintain shared memory between individual prompt requests.