Detect Crop Anomalies Instantly, Enhance Agricultural Data Integrity
Instantly identify anomalous crop images, preventing misclassification and saving hours of manual data validation per week.
Identifying novel or anomalous crops in large image datasets is a manual, error-prone, and time-consuming process. This workflow automates image anomaly detection by comparing new crop images against established cluster thresholds in a vector database, instantly flagging unknown varieties.
Documentation
AI-Powered Crop Anomaly Detection
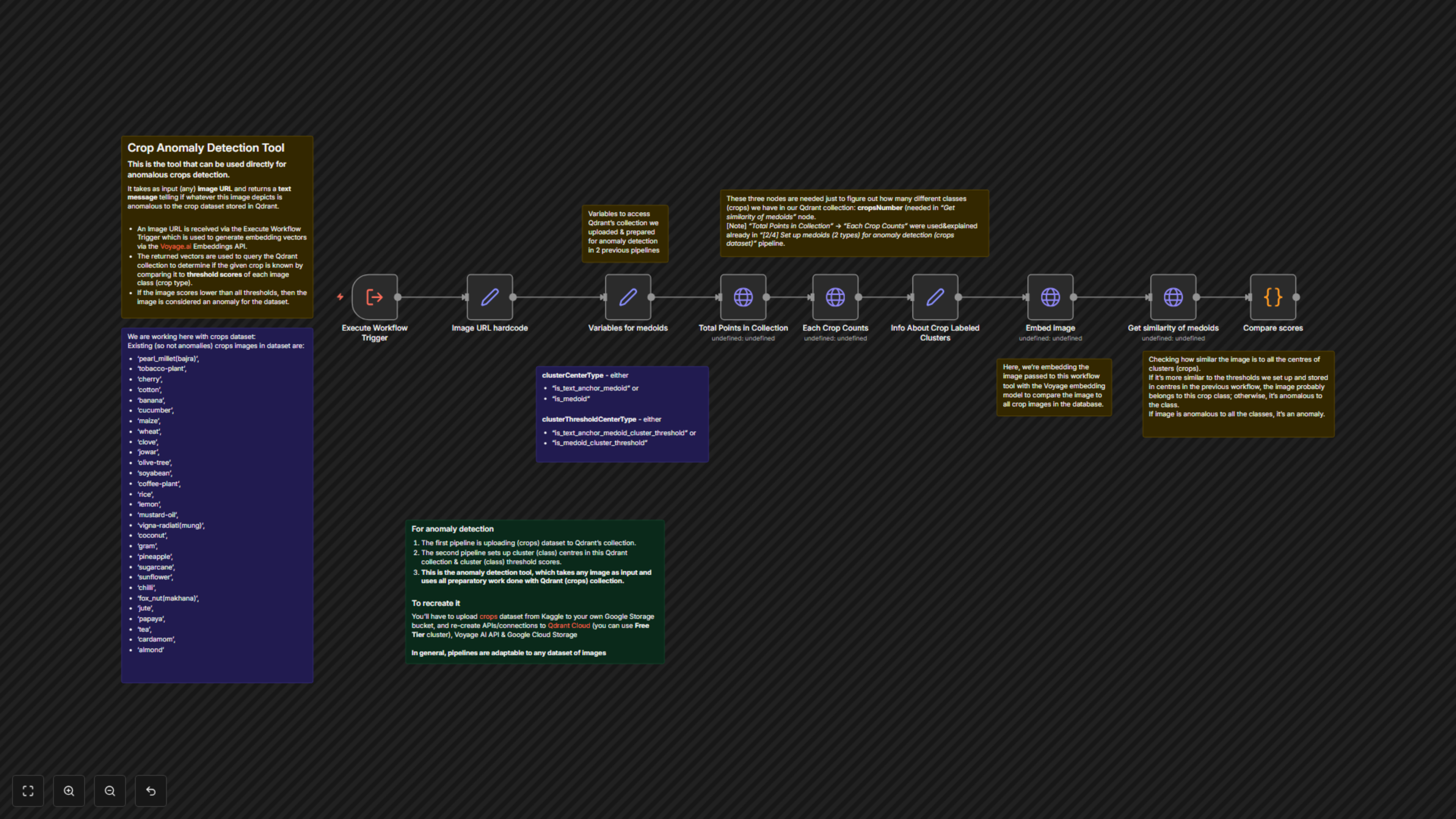
Identifying novel or anomalous crops in large agricultural image datasets can be a time-consuming and error-prone manual process. This n8n workflow provides a robust, automated solution for real-time anomaly detection, leveraging AI to instantly identify unknown crop varieties and ensure data purity. It's the final part of a three-workflow series designed to set up and utilize an image anomaly detection system, adaptable to any image dataset.
Key Features
- Real-time Image Embedding: Utilizes Voyage AI to convert input image URLs into high-dimensional vector embeddings for efficient analysis.
- Vector Database Integration: Seamlessly queries a Qdrant Cloud collection containing established crop medoids and their anomaly thresholds.
- Intelligent Anomaly Flagging: Automatically compares new image embeddings against predefined similarity thresholds for known crop classes, flagging any image that doesn't meet the criteria as a potential anomaly.
- Scalable & Adaptable: Designed for agricultural datasets but easily configurable for anomaly detection across any image-based classification task.
How It Works
Upon receiving an image URL via an Execute Workflow Trigger, the workflow first generates a multimodal embedding of the image using the Voyage AI API. This embedding is then sent to your Qdrant Cloud collection, where it queries for the most similar 'medoid' (cluster center) points representing known crop types. A Python code node meticulously compares the similarity score of the input image against each medoid's specific anomaly threshold. If the image's score falls below all established thresholds, it is classified and reported as a potential anomaly, signaling an undefined or new crop type.