Automate Medoid & Threshold Setup for Anomaly Detection
Reduce manual effort in identifying cluster centers and anomaly thresholds by 90%, enabling faster deployment of highly accurate anomaly detection systems.
Manually identifying optimal data points (medoids) and setting precise anomaly thresholds in large datasets is a time-consuming challenge. This n8n workflow automates both processes using two distinct AI approaches, streamlining the setup for robust anomaly detection in image datasets.
Documentation
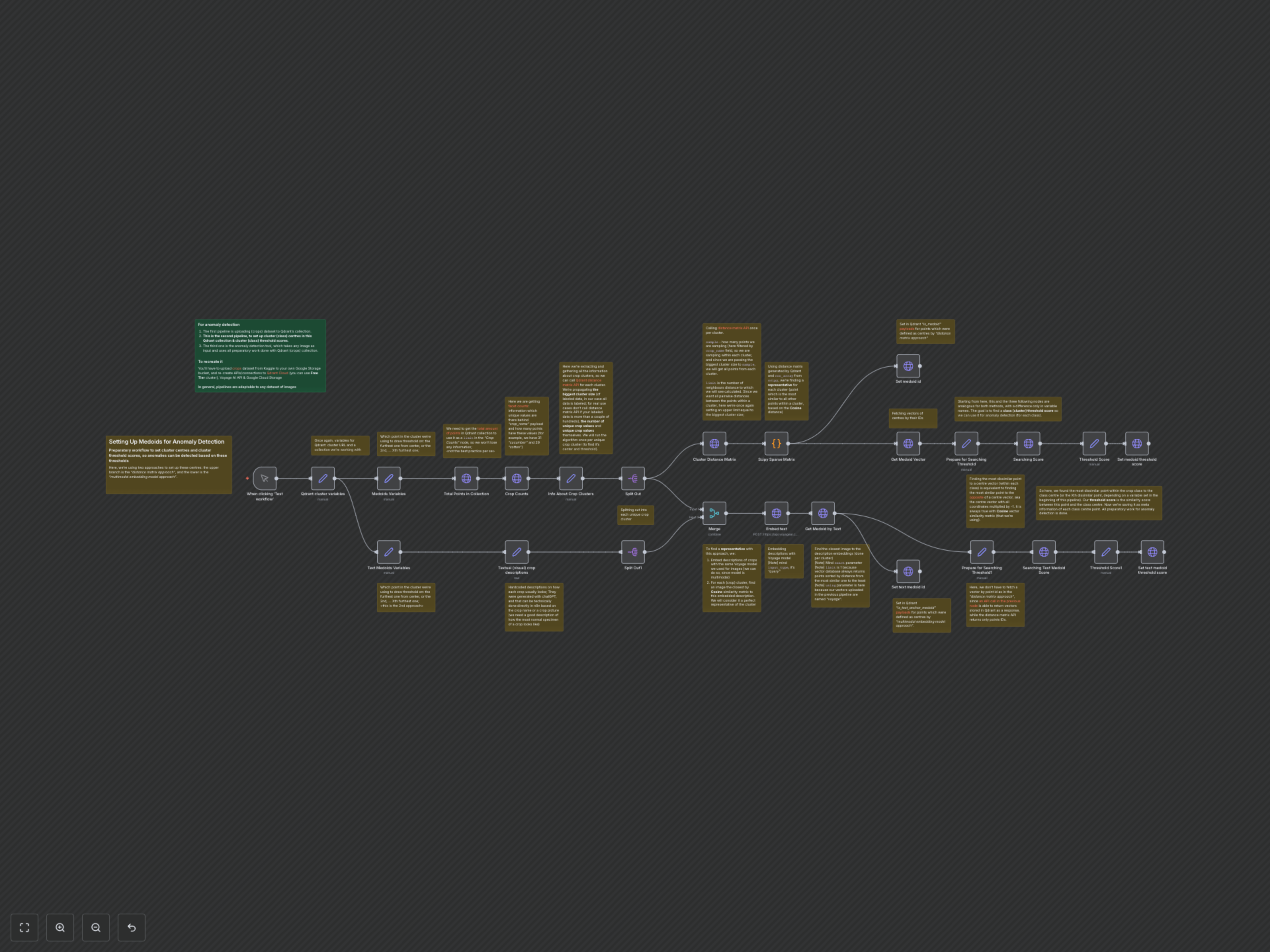
Setting Up Medoids for Anomaly Detection (Crops Dataset)
This n8n workflow is the crucial second step in a three-part anomaly detection system for agricultural crop images. It automates the complex process of identifying representative data points (medoids) and calculating precise anomaly detection thresholds within your Qdrant vector database, laying the groundwork for highly accurate outlier identification.
Key Features
- Automatically identifies optimal cluster centers (medoids) using two advanced methodologies: a distance matrix approach for vector similarity and a multimodal embedding model for text-to-image matching.
- Calculates and stores specific anomaly detection threshold scores for each crop cluster directly within your Qdrant collection payload, ready for real-time analysis.
- Supports robust anomaly detection setup for diverse image datasets, adaptable beyond agricultural crops with minimal configuration.
- Integrates seamlessly with Qdrant Cloud for efficient vector database operations and Voyage AI for powerful multimodal embeddings.
How It Works
The workflow initiates by fetching Qdrant cluster variables and obtaining total point counts and unique crop categories. It then processes each unique crop category in two parallel branches to define medoids and thresholds.
Distance Matrix Approach
For each crop cluster, the workflow queries Qdrant for a distance matrix of its points. A Python code node utilizes Scipy's `coo_array` to identify the medoid (the point most similar to all others within that cluster based on Cosine distance). This medoid's ID is then marked in Qdrant with an `is_medoid` payload. Its vector is fetched, and an "opposite vector" is calculated (all coordinates multiplied by -1). Finally, by searching for the point most similar to this opposite vector (equivalent to finding the furthest point from the medoid), the workflow establishes and saves the cluster's anomaly threshold score in Qdrant as `is_medoid_cluster_threshold`.
Multimodal Embedding Approach (Text Anchor Medoids)
In parallel, this branch uses pre-defined textual descriptions for each crop. These descriptions are embedded into vectors using Voyage AI's multimodal embedding model. For each crop cluster, the workflow then searches Qdrant to find the image vector most similar to its embedded text description, designating this image as the "text anchor medoid." Its ID is marked in Qdrant with an `is_text_anchor_medoid` payload. Similar to the first approach, its vector is used to find the point furthest from it, and its anomaly threshold score is calculated and stored in Qdrant as `is_text_anchor_medoid_cluster_threshold`. Both methods ensure that each crop cluster has robustly defined centers and thresholds for subsequent anomaly detection.